Testing
Chinstrap supports testing smart contracts with SmartPy, pytest and Ligo. Contracts programmed in Ligo can also be tested with pytest.
_ _ _
___| |__ (_)_ __ ___| |_ _ __ __ _ _ __
/ __| '_ \| | '_ \/ __| __| '__/ _` | '_ \
| (__| | | | | | | \__ \ |_| | | (_| | |_) |
\___|_| |_|_|_| |_|___/\__|_| \__,_| .__/
|_|
🐧 Chinstrap - a cute framework for developing Tezos Smart Contracts!
usage: main.py test [-h] [-t TEST] [-l] [-e ENTRYPOINT]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-t TEST, --test TEST Test to run. If not specified, all the tests are executed
-l, --local Run tests on host machine. If not specified, Docker image
is preferred
-e ENTRYPOINT, --entrypoint ENTRYPOINT
Entrypoint to use when compiling Ligo contracts. Default
entrypoint is main
Tests are placed in tests folder. Tests written in Python using SmartPy/Pytest have .py extension and tests written in
cameligo, pascaligo, reasonligo and jsligo have respective extensions. The taest engine is configured in chinstrap-config.yml as shown:
chinstrap:
network:
development:
host: http://localhost:12345
accounts:
- privateKeyFile: ./.secret
compiler:
lang: smartpy
test: pytest
The above configuration uses SmartPy for compiling the contracts and PyTest as testing engine.
A typical testing scenario consists in:
initializing the context (starting servers, setting up clients)
running a sequence of commands and assertions
releasing resources, terminating servers
Basic things to keep in mind while writing tests:
- Write your tests. Keep in mind these few basic rules:
- A test must check only one behavior at a time.
- One test = one method.
- No magic number: all the values used must be declared in variables, with explicit names.
- There can be no useless variables to pass the test. If a variable can be removed without making the test fail, it must be removed.
- The method name must be explicit. Anyone should understand what the test takes as input, what behavior is been checked and what result is expected.
- A test can be divided into three parts (as implemented in the tests below):
- GIVEN: input declarations, expected results
- WHEN: the tested method is called with the declared inputs
- THEN: assertions checks
Testing: SmartPy
A SmartPy test file consists of tests and screnarios under the test. A test is defined as a Python method under a sp.add_test(name, shortname=None, profile=False, is_default=True) decorator. Scenarios are defiend inside the test methods.
Initially we import the contract we would like to test. We can do this inside the test file by using sp.io.import_script_from_url (url) method provided by SmartPy. Here, the argument url is a string of the form http://, https://, file://, file:, etc. For writing tests using SmartPy, please follow the instructions on SmartPy
contract = sp.io.import_script_from_url("file:contracts/SampleContract.py")
To define a test, we define a Python function and add @sp.add_test(name = "A Test") decorator. Here name is the name of the test.
@sp.add_test(name = "A Test")
def test():
To define a scenario in a test, we use sp.test_scenario method to create a scenario object. Scenarios describe a sequence of actions.
@sp.add_test(name = "A Test")
def test():
scenario = sp.test_scenario()
We have to register the contract we imported for this scenario.
@sp.add_test(name = "A Test")
def test():
# create a scenario
scenario = sp.test_scenario()
#instantiate a contract
c1 = MyContract()
# add the contract to the scenario
scenario += c1 # which is equivalent to `scenario.register(c1, show = True)`
# To only register the smart contract but not show it
scenario.register(c1)
Final test file looks like this:
contract = sp.io.import_script_from_url("file:contracts/SampleContract.py")
@sp.add_test(name = "A Test")
def test():
# Create a scenario
scenario = sp.test_scenario()
# Instantiate a contract
c1 = MyContract()
# Add the contract to the scenario
scenario += c1 # which is equivalent to `scenario.register(c1, show = True)`
# To only register the smart contract but not show it
scenario.register(c1)
Output:

Testing: PyTest
In PyTest, we define testing scenarios by grouping tests in a class, and managing the context in a fixture.
Currently, all tests scenarios in the PyTest suite are defined as classes that inheri TestCase from unittest, consisting of a sequence of methods that are run incrementally (as specified with the annotation @pytest.mark.incremental).
Classes are used to define the scope of a fixture, and a unit of incremental testing sequence. We don’t directly instantiate them, or use self.
Data between methods are shared using a dictionary session. For instance, we save the result of the transfer operation, and retrieve it in the next method.
We define a class by inheriting TestCase from unitest module. You can name this class whatever you want but try to keep it descriptive.
from unittest import TestCase
class SampleContractTests(TestCase):
We have to declare a @classmethod named setUpClass which will be called by Chinstrap. In this method, we fetch the target contract to we want to test.
from unittest import TestCase
from chinstrap.tests import getContractInterface
class SampleContractTests(TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls):
cls.contract = getContractInterface("SampleContract")
Now we can define a method in the test class, taht uses self.contract to call contract methods we would like to test. Also, with unittest, a test method name should start with test_ , otherwise it will not be considered as a test.
For example, if we want to test the increment function inside the contract, and verify the result, the test method looks like this:
def test_should_pass_if_the_return_value_is_5(self):
value = 5
storage = {"owner": owner, "counter": 0}
result = self.contract.increment(value).interpret(storage=storage, source=owner)
assert result.storage["counter"] == 5
Final test file looks like this:
from unittest import TestCase
from pytezos import MichelsonRuntimeError
from chinstrap.tests import getContractInterface
owner = "tz1YtuZ4vhzzn7ssCt93Put8U9UJDdvCXci4"
alice = "tz1LFuHW4Z9zsCwg1cgGTKU12WZAs27ZD14v"
class SampleContractTests(TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls):
cls.contract = getContractInterface("SampleContract")
def test_should_pass_if_the_return_value_is_5(self):
value = 5
storage = {"owner": owner, "counter": 0}
result = self.contract.increment(value).interpret(storage=storage, source=owner)
assert result.storage["counter"] == 5
def test_should_fail_if_the_source_is_not_the_owner(self):
value = 5
storage = {"owner": owner, "counter": 0}
with self.assertRaises(MichelsonRuntimeError) as context:
self.contract.increment(value).interpret(storage=storage, source=alice)
self.assertEqual(
context.exception.args[-1].strip("\\").strip("'"),
"Only owner can increment",
)
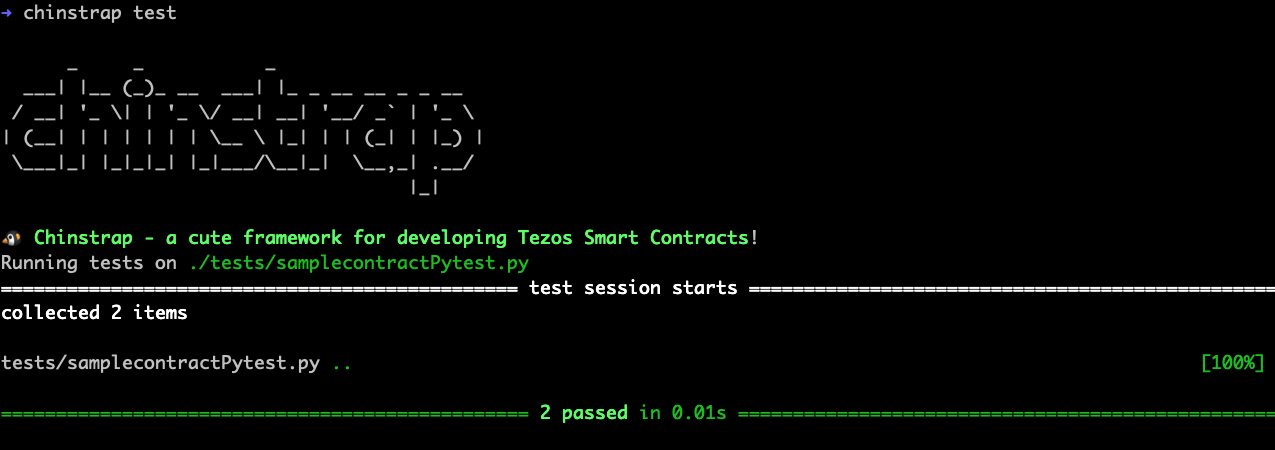
Output:
Testing: Ligo
Let's use FA1.2.mligo contract from ligolang's repo.
Create a file name MyContract.mligo inside contracts/ folder and paste the following code and save.
// This is MyContract.mligo
type transfer =
[@layout:comb]
{ [@annot:from] address_from : address;
[@annot:to] address_to : address;
value : nat }
type approve =
[@layout:comb]
{ spender : address;
value : nat }
type allowance_key =
[@layout:comb]
{ owner : address;
spender : address }
type getAllowance =
[@layout:comb]
{ request : allowance_key;
callback : nat contract }
type getBalance =
[@layout:comb]
{ owner : address;
callback : nat contract }
type getTotalSupply =
[@layout:comb]
{ request : unit ;
callback : nat contract }
type tokens = (address, nat) big_map
type allowances = (allowance_key, nat) big_map
type storage = {
tokens : tokens;
allowances : allowances;
total_supply : nat;
}
type parameter =
| Transfer of transfer
| Approve of approve
| GetAllowance of getAllowance
| GetBalance of getBalance
| GetTotalSupply of getTotalSupply
type result = operation list * storage
[@inline]
let positive (n : nat) : nat option =
if n = 0n
then (None : nat option)
else Some n
let transfer (param, storage : transfer * storage) : result =
let allowances = storage.allowances in
let tokens = storage.tokens in
let allowances =
if Tezos.sender = param.address_from
then allowances
else
let allowance_key = { owner = param.address_from ; spender = Tezos.sender } in
let authorized_value =
match Big_map.find_opt allowance_key allowances with
| Some value -> value
| None -> 0n in
let authorized_value =
match is_nat (authorized_value - param.value) with
| None -> (failwith "NotEnoughAllowance" : nat)
| Some authorized_value -> authorized_value in
Big_map.update allowance_key (positive authorized_value) allowances in
let tokens =
let from_balance =
match Big_map.find_opt param.address_from tokens with
| Some value -> value
| None -> 0n in
let from_balance =
match is_nat (from_balance - param.value) with
| None -> (failwith "NotEnoughBalance" : nat)
| Some from_balance -> from_balance in
Big_map.update param.address_from (positive from_balance) tokens in
let tokens =
let to_balance =
match Big_map.find_opt param.address_to tokens with
| Some value -> value
| None -> 0n in
let to_balance = to_balance + param.value in
Big_map.update param.address_to (positive to_balance) tokens in
(([] : operation list), { storage with tokens = tokens; allowances = allowances })
let approve (param, storage : approve * storage) : result =
let allowances = storage.allowances in
let allowance_key = { owner = Tezos.sender ; spender = param.spender } in
let previous_value =
match Big_map.find_opt allowance_key allowances with
| Some value -> value
| None -> 0n in
begin
if previous_value > 0n && param.value > 0n
then (failwith "UnsafeAllowanceChange")
else ();
let allowances = Big_map.update allowance_key (positive param.value) allowances in
(([] : operation list), { storage with allowances = allowances })
end
let getAllowance (param, storage : getAllowance * storage) : operation list =
let value =
match Big_map.find_opt param.request storage.allowances with
| Some value -> value
| None -> 0n in
[Tezos.transaction value 0mutez param.callback]
let getBalance (param, storage : getBalance * storage) : operation list =
let value =
match Big_map.find_opt param.owner storage.tokens with
| Some value -> value
| None -> 0n in
[Tezos.transaction value 0mutez param.callback]
let getTotalSupply (param, storage : getTotalSupply * storage) : operation list =
let total = storage.total_supply in
[Tezos.transaction total 0mutez param.callback]
let main (param, storage : parameter * storage) : result =
begin
if Tezos.amount <> 0mutez
then failwith "DontSendTez"
else ();
match param with
| Transfer param -> transfer (param, storage)
| Approve param -> approve (param, storage)
| GetAllowance param -> (getAllowance (param, storage), storage)
| GetBalance param -> (getBalance (param, storage), storage)
| GetTotalSupply param -> (getTotalSupply (param, storage), storage)
end
Let's say we want to test the above MyContract contract using JsLigo.
Let's create a test file in tests/ folder and name it MyContract.test.jsligo.
#import "../contracts/MyContract.jsligo" "Test"
let _test = () : bool => {
let initial_storage = 42 as int;
let [taddr, _, _] = Test.originate(Test.main, initial_storage, 0 as tez);
return (Test.get_storage(taddr) == initial_storage);
};
let test = _test();
Now we configure the chinstrap-config.yaml file to use cameligo as compiler and as test engine.
chinstrap:
network:
development:
host: http://localhost:12345
accounts:
- privateKeyFile: ./.secret
compiler:
lang: cameligo
test: cameligo
Chinstrap now uses CameLigo to compile and test the contracts.
To define a test for this contract, we include the contents of this contract into our test file.
// MyContract.test.mligo
#include "../contracts/MyContract.mligo"
and define the test as shown here
// MyContract.test.mligo
#include "../contracts/MyContract.mligo"
let test_transfer =
let () = Test.reset_state 10n ([] : tez list) in
let sender_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 0 in
let from_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 1 in
let to_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 2 in
let storage = { tokens = Big_map.literal [(sender_, 100n); (from_, 100n); (to_, 100n)];
allowances = Big_map.literal [({ owner = from_; spender = sender_ }, 100n)];
total_supply = 300n } in
let (typed_addr, _, _) = Test.originate main storage 0tez in
let contr = Test.to_contract typed_addr in
let parameter = Transfer { address_from = from_; address_to = to_; value = 10n } in
let () = Test.set_source sender_ in
let _ = Test.transfer_to_contract_exn contr parameter 0tez in
let new_storage = Test.get_storage typed_addr in
assert ((Big_map.find_opt to_ new_storage.tokens = Some 110n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt from_ new_storage.tokens = Some 90n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt sender_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt ({ owner = from_; spender = sender_ }) new_storage.allowances = Some 90n) &&
(new_storage.total_supply = 300n))
let test_transfer_not_e_allowance =
let () = Test.reset_state 10n ([] : tez list) in
let sender_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 0 in
let from_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 1 in
let to_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 2 in
let storage = { tokens = Big_map.literal [(sender_, 100n); (from_, 100n); (to_, 100n)];
allowances = Big_map.literal [({ owner = from_; spender = sender_ }, 0n)];
total_supply = 300n } in
let (typed_addr, _, _) = Test.originate main storage 0tez in
let contr = Test.to_contract typed_addr in
let parameter = Transfer { address_from = from_; address_to = to_; value = 10n } in
let () = Test.set_source sender_ in
match Test.transfer_to_contract contr parameter 0tez with
| Success _ -> failwith "Transaction should fail"
| Fail (Rejected (a, _)) -> assert (Test.michelson_equal a (Test.eval "NotEnoughAllowance"))
| Fail _ -> failwith "Transaction should fail with rejection"
let test_transfer_not_e_balance =
let () = Test.reset_state 10n ([] : tez list) in
let sender_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 0 in
let from_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 1 in
let to_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 2 in
let storage = { tokens = Big_map.literal [(sender_, 100n); (from_, 0n); (to_, 100n)];
allowances = Big_map.literal [({ owner = from_; spender = sender_ }, 100n)];
total_supply = 300n } in
let (typed_addr, _, _) = Test.originate main storage 0tez in
let contr = Test.to_contract typed_addr in
let parameter = Transfer { address_from = from_; address_to = to_; value = 10n } in
let () = Test.set_source sender_ in
match Test.transfer_to_contract contr parameter 0tez with
| Success _ -> failwith "Transaction should fail"
| Fail (Rejected (a, _)) -> assert (Test.michelson_equal a (Test.eval "NotEnoughBalance"))
| Fail _ -> failwith "Transaction should fail with rejection"
let test_approve =
let () = Test.reset_state 10n ([] : tez list) in
let sender_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 0 in
let from_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 1 in
let to_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 2 in
let storage = { tokens = Big_map.literal [(sender_, 100n); (from_, 100n); (to_, 100n)];
allowances = Big_map.literal [({ owner = sender_; spender = from_ }, 0n)];
total_supply = 300n } in
let (typed_addr, _, _) = Test.originate main storage 0tez in
let contr = Test.to_contract typed_addr in
let parameter = Approve { spender = from_; value = 100n } in
let () = Test.set_source sender_ in
let _ = Test.transfer_to_contract_exn contr parameter 0tez in
let new_storage = Test.get_storage typed_addr in
assert ((Big_map.find_opt to_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt from_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt sender_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt ({ owner = sender_; spender = from_ }) new_storage.allowances = Some 100n) &&
(new_storage.total_supply = 300n))
let test_approve_unsafe =
let () = Test.reset_state 10n ([] : tez list) in
let sender_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 0 in
let from_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 1 in
let to_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 2 in
let storage = { tokens = Big_map.literal [(sender_, 100n); (from_, 100n); (to_, 100n)];
allowances = Big_map.literal [({ owner = sender_; spender = from_ }, 100n)];
total_supply = 300n } in
let (typed_addr, _, _) = Test.originate main storage 0tez in
let contr = Test.to_contract typed_addr in
let parameter = Approve { spender = from_; value = 100n } in
let () = Test.set_source sender_ in
match Test.transfer_to_contract contr parameter 0tez with
| Success _ -> failwith "Transaction should fail"
| Fail (Rejected (a, _)) -> assert (Test.michelson_equal a (Test.eval "UnsafeAllowanceChange"))
| Fail _ -> failwith "Transaction should fail with rejection"
let test_get_allowance =
let dummy_contract (v, s : nat * nat) : operation list * nat = ([] : operation list), v + s in
let () = Test.reset_state 10n ([] : tez list) in
let sender_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 0 in
let from_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 1 in
let to_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 2 in
let (dummy_typed_addr, _, _) = Test.originate dummy_contract 0n 0tez in
let dummy_typed_contr = Test.to_contract dummy_typed_addr in
let storage = { tokens = Big_map.literal [(sender_, 100n); (from_, 100n); (to_, 100n)];
allowances = Big_map.literal [({ owner = from_; spender = sender_ }, 100n)];
total_supply = 300n } in
let (typed_addr, _, _) = Test.originate main storage 0tez in
let contr = Test.to_contract typed_addr in
let parameter = GetAllowance { request = { owner = from_; spender = sender_} ; callback = dummy_typed_contr } in
let () = Test.set_source sender_ in
let _ = Test.transfer_to_contract_exn contr parameter 0tez in
let new_storage = Test.get_storage typed_addr in
let _ = assert ((Big_map.find_opt to_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt from_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt sender_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt ({ owner = from_; spender = sender_ }) new_storage.allowances = Some 100n) &&
(new_storage.total_supply = 300n)) in
let dummy_new_storage = Test.get_storage dummy_typed_addr in
assert (dummy_new_storage = 100n)
let test_get_balance =
let dummy_contract (v, s : nat * nat) : operation list * nat = ([] : operation list), v + s in
let () = Test.reset_state 10n ([] : tez list) in
let sender_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 0 in
let from_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 1 in
let to_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 2 in
let (dummy_typed_addr, _, _) = Test.originate dummy_contract 0n 0tez in
let dummy_typed_contr = Test.to_contract dummy_typed_addr in
let storage = { tokens = Big_map.literal [(sender_, 100n); (from_, 100n); (to_, 100n)];
allowances = Big_map.literal [({ owner = sender_; spender = from_ }, 100n)];
total_supply = 300n } in
let (typed_addr, _, _) = Test.originate main storage 0tez in
let contr = Test.to_contract typed_addr in
let parameter = GetBalance { owner = from_ ; callback = dummy_typed_contr } in
let () = Test.set_source sender_ in
let _ = Test.transfer_to_contract_exn contr parameter 0tez in
let new_storage = Test.get_storage typed_addr in
let _ = assert ((Big_map.find_opt to_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt from_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt sender_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt ({ owner = sender_; spender = from_ }) new_storage.allowances = Some 100n) &&
(new_storage.total_supply = 300n)) in
let dummy_new_storage = Test.get_storage dummy_typed_addr in
assert (dummy_new_storage = 100n)
let test_get_total_supply =
let dummy_contract (v, s : nat * nat) : operation list * nat = ([] : operation list), v + s in
let () = Test.reset_state 10n ([] : tez list) in
let sender_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 0 in
let from_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 1 in
let to_ = Test.nth_bootstrap_account 2 in
let (dummy_typed_addr, _, _) = Test.originate dummy_contract 0n 0tez in
let dummy_typed_contr = Test.to_contract dummy_typed_addr in
let storage = { tokens = Big_map.literal [(sender_, 100n); (from_, 100n); (to_, 100n)];
allowances = Big_map.literal [({ owner = sender_; spender = from_ }, 100n)];
total_supply = 300n } in
let (typed_addr, _, _) = Test.originate main storage 0tez in
let contr = Test.to_contract typed_addr in
let parameter = GetTotalSupply { callback = dummy_typed_contr; request = () } in
let () = Test.set_source sender_ in
let _ = Test.transfer_to_contract_exn contr parameter 0tez in
let new_storage = Test.get_storage typed_addr in
let _ = assert ((Big_map.find_opt to_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt from_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt sender_ new_storage.tokens = Some 100n) &&
(Big_map.find_opt ({ owner = sender_; spender = from_ }) new_storage.allowances = Some 100n) &&
(new_storage.total_supply = 300n)) in
let dummy_new_storage = Test.get_storage dummy_typed_addr in
assert (dummy_new_storage = 300n)
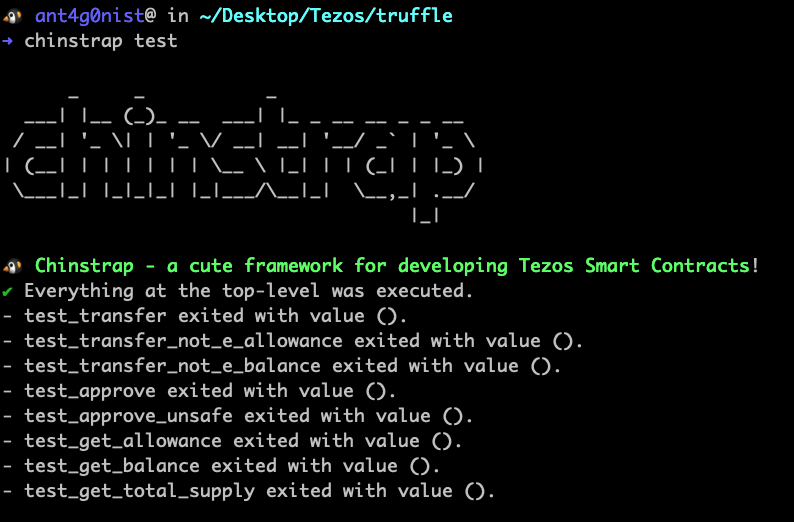
Now let's run chinstrap test to run above defined tests.
Happy testing 🧪