Slides are available here:
Tezos development with Chinstrap

- Docs 📖 : https://chinstrap.io/docs
- Tele 💬 : https://t.me/chinstrap_io
Slides are available here:
Tezos development with Chinstrap

We developed, tested, and originated a FA1.2 contract to our Flextesa sandbox in our previous post. In this post, we will do the same, but instead of using Chinstrap cli, we will use Chinstrap REPL.
Please read the Part-1 of this 2-part series on how to use Chinstrap to create, test and deploy Tezos smart contracts.
Chinstrap's read–eval–print loop (REPL) is a simple interactive development environment that takes a single command/method call, executes them, and returns the result. Using repl makes interacting with the deployed contracts on the chain easy.
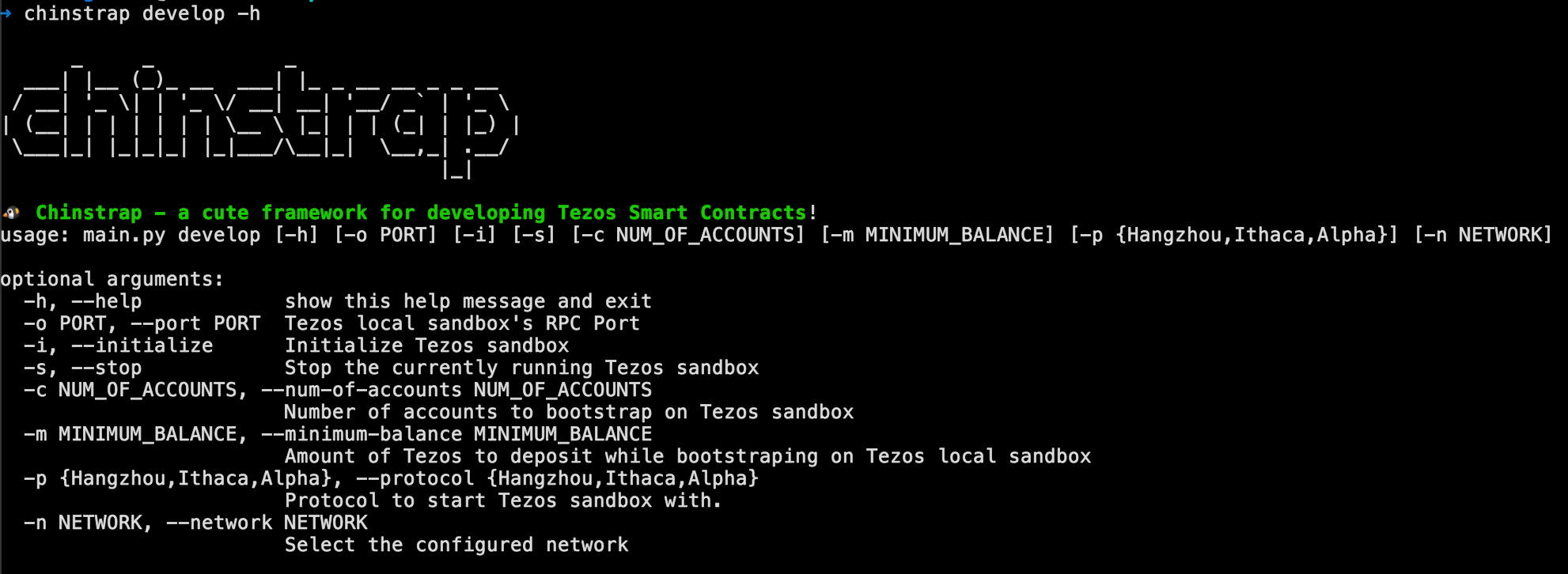
Chinstrap provides a develop sub-command that provides a repl to develop interactively. chinstrap develop launches a powerful repl, exposing Chinstrap's functionality to the repl, making the interaction with Tezos networks much more effortless.
chinstrap develop -h
Please clone the ChinToken repo from ant4g0nist/ChinToken.
When we launch Chinstrap's repl, we can either start the Flextesa sandbox or directly connect to any configured network in chinstrap-config.yml file.
The following process remains for all the networks.
The configuration for the local development should like:
chinstrap:
network:
development:
host: http://localhost:20000
accounts:
- privateKeyFile: ./.secret
compiler:
lang: smartpy
test: smartpy
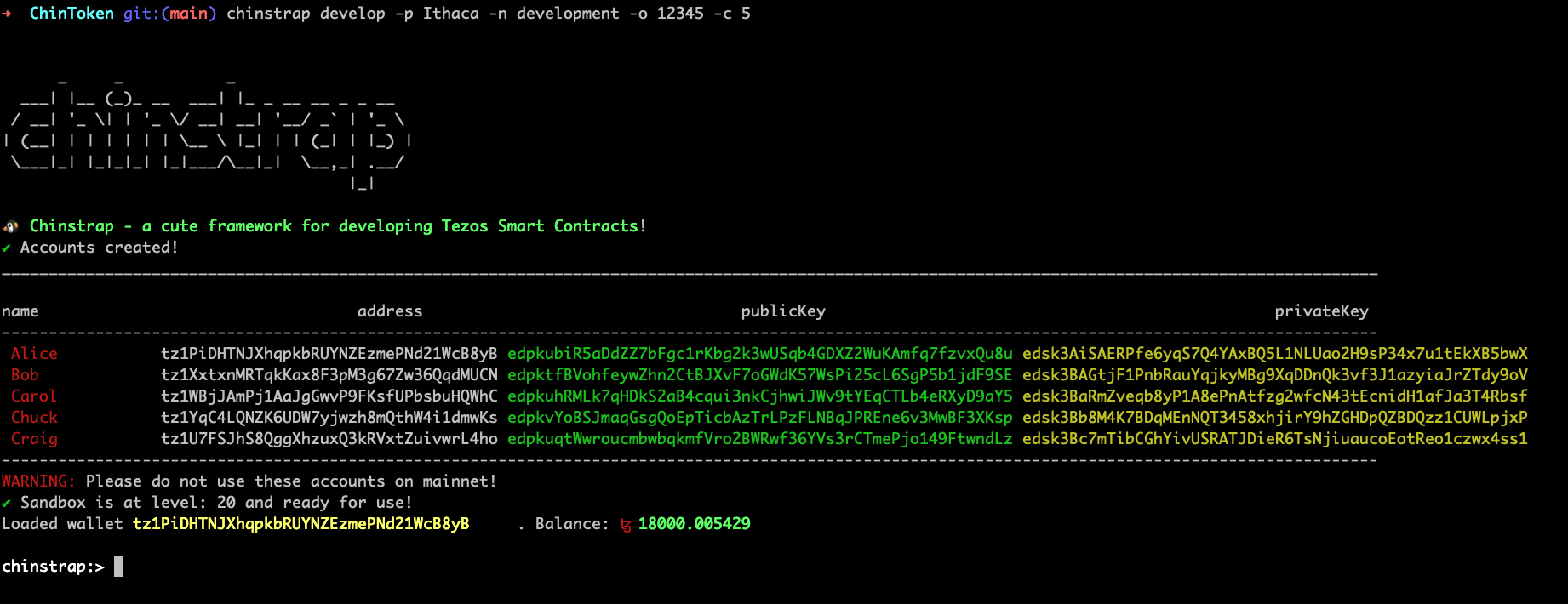
To start a local sandbox on port 20000, generate 5 test accounts and use Ithaca protocol, and launch the repl, run the following command:
chinstrap develop -p Ithaca -n development -o 20000 -c 5
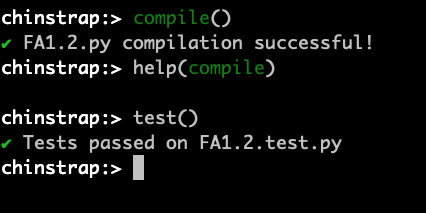
Chinstrap repl also has a compile function that compiles contracts inside contracts folder.
chinstrap:> compile()
✔ FA1.2.py compilation successful!
chinstrap:>
Chinstrap repl also has a test function that runs tests inside the tests folder.
chinstrap:> test()
✔ Tests passed on FA1.2.test.py
chinstrap:>
Chinstrap repl provides originate method to originate contracts.
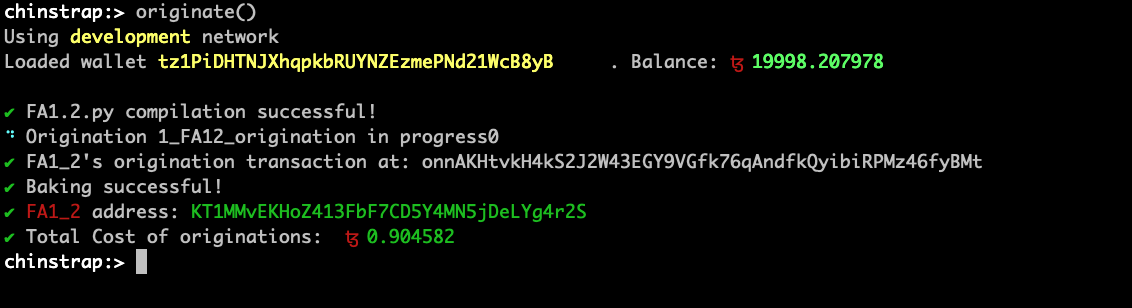
Now that we have originated the contract, things get a little more interesting. We can use the repl interface to interact with the contract.
Chinstrap exposes getContractFromAddress function through which we can get the contract interface from an address.
chinstrap:> contract = getContractFromAddress('KT1MMvEKHoZ413FbF7CD5Y4MN5jDeLYg4r2S')
Now you can inspect and call the FA1.2 entrypoints on the contract object.
For example, to access the contract's storage:
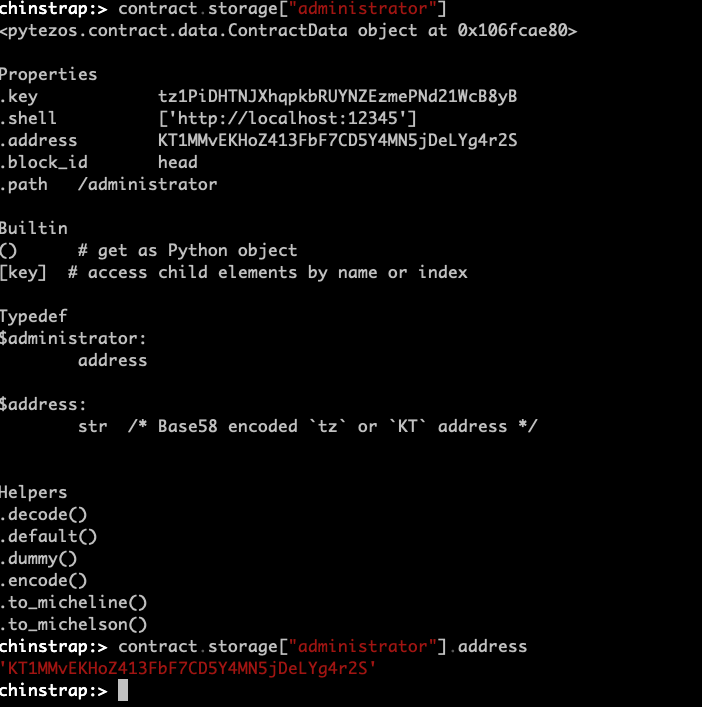
For further reading on all the available methods in the REPL, please check chinstrap/repl and (Inspecting Tezos smart contracts with PyTezos library)[https://baking-bad.org/blog/2019/03/24/inspecting-tezos-smart-contracts-with-pytezos-library/]
Stop the sandbox after the completion of testing.
chinstrap:> stopSandbox()
or
Run this in after exiting the repl:
chinstrap sandbox -s
Chinstrap's REPL is a more excellent way to interactively work with your contracts for testing and compiling or executing transactions by hand. Chinstrap's integration with Sandbox and Pytezos makes it a cleaner and more accessible interface for developing in the Tezos environment.
Join the telegram for further discussions: https://t.me/chinstrap_io Follow us on Twitter for continuous updates: https://twitter.com/chinstrap_io
Happy Hacking 👾 🎉